Payment processing refers to the behind-the-scenes process that enables merchants to accept payments from their customers, including credit and debit card transactions.
Although it appears simple and seamless for consumers, payment processing involves a complex series of systems and steps that work together to ensure secure and efficient transactions.
In this article, we will simplify payment processing and provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of how it works, including the different stages involved, how they interact with businesses and consumers, and how to prepare your business to accept electronic payments confidently.
You will learn the following;
- What is payment processing?
- The main entities involved in payment processing [+ their role]
- How does an online transaction work?
- Payment processing stats: A look at key metrics and trends
- Why does your business need payment processing?
- Benefits of payment processing
- How to choose the best payment processing solution
- Frequently Asked Questions for Payment Processing
Table of Contents
- What is payment processing?
- The main entities involved in payment processing
- How does an online transaction work?
- Payment processing stats: A look at key metrics and trends
- Why does your business need payment processing?
- Benefits of integrating payment processing
- Here is how you can choose the best payment processing solution
- Frequently asked questions related to payment processing
What is payment processing?
Payment processing refers to the activities involved in transferring funds from a customer to a merchant. For customers, payment processing might seem as simple as a credit or debit card tap, swipe, or tap, merely taking a few seconds.
However, for a business, it’s more than that. It involves several steps and entities, like:
- Cardholder (or buyer)
- Merchant (or seller)
- Issuing bank (Issuer)
- Acquiring bank (Acquirer)
- Payment processors
- Payment gateways
- Card networks (Visa, Mastercard, etc.)
Each entity plays a specific role in the payment process and works together to facilitate a secure and efficient transaction.
That’s a lot, right? As a business owner, you need to understand all the steps involved in processing a payment. But, before all that, let’s discuss the entities involved in processing payments.
The main entities involved in payment processing
Simply put, in debit or credit card processing, whether online, through phone sales, or even in person, there are three main players:
On one side is you, the business owner or merchant, while on the other is your customer. And, in between lies the technology that bridges the two of you.
1. You, the merchant
To accept credit and debit card payments from online customers, you’ll likely need a merchant bank (also termed as the acquirer) that accepts payments on your behalf and deposits them into the provided merchant account.
2. Your customer’s bank accounts
For your customer to pay for the services and goods, they need a credit or a debit card. The bank that approves them for the card payments and credits them the cash to pay you is known as an issuing bank.
3. The technology
Between lies the two technologies that allow you and your customer to make a transaction.
First is the payment gateway, a software that links your website shopping cart to the processing network. Next comes the payment processors (or merchant service), which do all the leg work like moving the transaction through the processing network, working with the bank, sending a billing statement, doing debit or credit card processing, etc.
The final outcome is a customer who successfully purchases without cash and a business that completes a sale.
How does an online transaction work?
On the surface, payment processing seems simple, but there’s much more than swiping or tapping debit or credit cards. It includes services like authorization, funding, and settling of a transaction.
Here’s what happens when a customer makes a purchase:
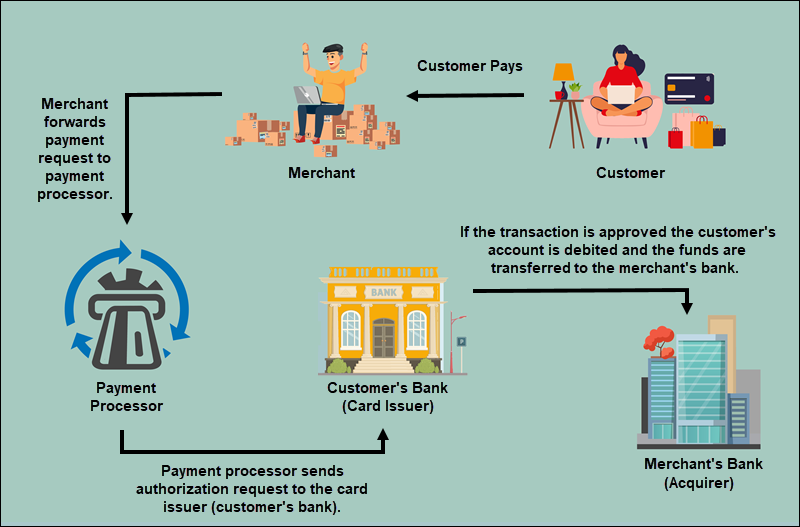
When a customer makes a purchase, the payment is made with the card at the point of sale, popularly known as POS. Though the transaction takes a second, the process behind the trade is intricate.
#Step 1: Engage at the point of sale system
The point of Sale system is the time and place where a retail transaction is completed.
So, payment methods at a point of sale vary from debit or credit card payments to online payments, checks, cash, etc. Consumers are using digital payment methods to make in-store and online purchases.
According to new projections from PwC, the volume of cashless payment transactions globally is predicted to surge by more than 80% between 2020 and 2025, expected from 1 trillion to 1.9 trillion.
#Step 2: Connecting to a payment gateway
A payment gateway is a mechanism that reads and transfers payment information from a customer’s to a merchant’s bank account.
#Step 3: Payment processor comes into the picture
The merchant sends a request to their respective payment processor for the authorization of the transaction. Further, the payment processor carries out essential steps:
- The payment processor submits the transaction to the respective card association associated with the issuing bank.
- The issuing bank accepts or rejects the payment based on pre-set parameters.
- Next, the issuing bank sends either an approval or a rejection status back to the merchant bank and finally makes it to the merchant account.
# Step 4: Transfer funds to the merchant account
The process of settling and funding comes when a transaction is processed and approved. This is actually where the transaction is deposited into the merchant’s account.
The card association is related to the issuing bank; therefore, the issuing bank receives the transaction details and further carries out the process, which consists of:
- The issuing bank charges a defined sum from the cardholders for the transaction.
- Then the issuing bank transfers the appropriate amount to the merchant bank, subtracting the interchange fee.
- The merchant bank transmits the amount to the merchant account.
The complete process happens quickly between the time the order is placed and the receipt handed to the customer.
Payment processing stats: A look at key metrics and trends
- According to Visa, Tap-To-Pay transactions have grown 30% over the past years.
- Nearly 50% of US shoppers say they won’t shop at a store that doesn’t offer a cashless way to shop.
- According to Statista, global e-commerce sales are expected to reach 8.1 trillion dollars by 2026.
Below you can find some major key payment processing stats on how US customers will pay for goods and services moving forward;
1. Credit card processing
Credit card processing is a system through which data from the customer’s credit card is transmitted for approving a dollar transaction from their bank account to the merchant account.
While there was a dip in in-store credit card transactions during the pandemic, Insider Intelligence predicted that the value would reach $2, 223.43 in 2022.
2. Online payment processing
Online payment processing links a website with a payment processor to connect a merchant account to a credit and debit card issuer. Furthermore, merchant accounts can set up recurring payments, accept or decline transactions according to pre-set parameters, and process payments made with foreign currency.

Furthermore, the epidemic accelerated the adoption of mobile payment platforms as Americans sought out retailers offering contactless services. As a result, users, as well as transaction value growth, have accelerated.
3. ACH payment processing
ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a network that routes payments electronically between banks across the United States. Typically, there are two types of ACH payments:
- Credit ACH Payments
- Debit ACH Payments
Conventionally, ACH was developed as a way for banks to process paper checks digitally. But, since it has become digitally reliant, with online ACH including 27.9% of transactions by volume in the third Quarter of 2020, as per the NACHA (National Automated Clearing House Association), ACH is growing not only in segments like disbursements, bill pay, and direct deposit but also for digital P2P transactions and online transfers.
To put in all, ACH is emerging, not just in check-based segments like bill pay, disbursements, and direct deposits, but also for online and digital P2P transactions.
4. Merchant payment processing
Merchant payment providers let merchants easily accept credit and debit card payments and all other forms of payment from consumers. While merchant acquirers allow payment transactions, merchant payment processors are responsible for securely transmitting data related to those transactions and offering several degrees of back-office support.
For example, PayPal’s growth amid the pandemic witnessed an unprecedented rise as merchants relied on the firm to facilitate transactions. But, as of August 2021, PayPal changed its fee structure, making merchants pay $3.98 in fees for a $100 transaction, compared to $3.20 before.
This change made merchants think of leaving PayPal and switching to reliable payment service providers like GETTRX, which offer their own processing services. The best option significantly depends on your business sales volume and payment accepting method.
Why does your business need payment processing?
Practically for every business, it’s a matter of when?
As customer preferences for making payments continuously evolve away from cash and check transactions, it just makes sense to have electronic payments flow into the business accounting system.
Exhibit 1: US customers prefer more digital commerce
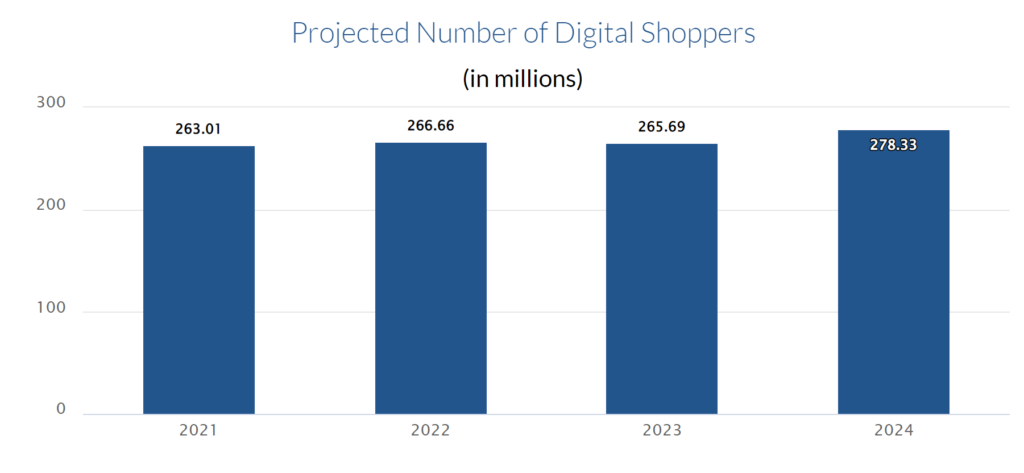
Data source: Finances Online
Exhibit 2: Omnichannel digital payment adoption has grown exceptionally
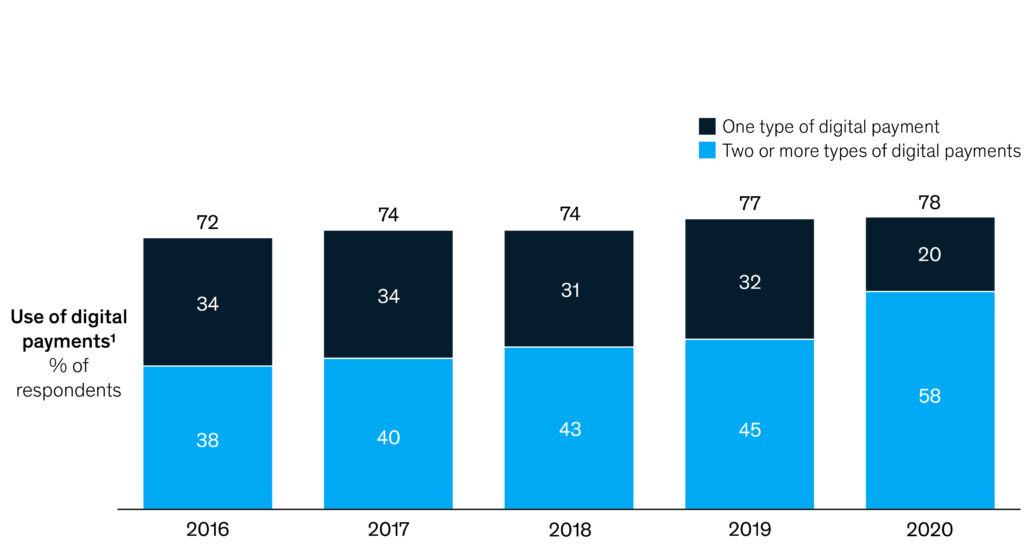
Data source: Mckinsey
Exhibit 3: Contactless payments are gaining share
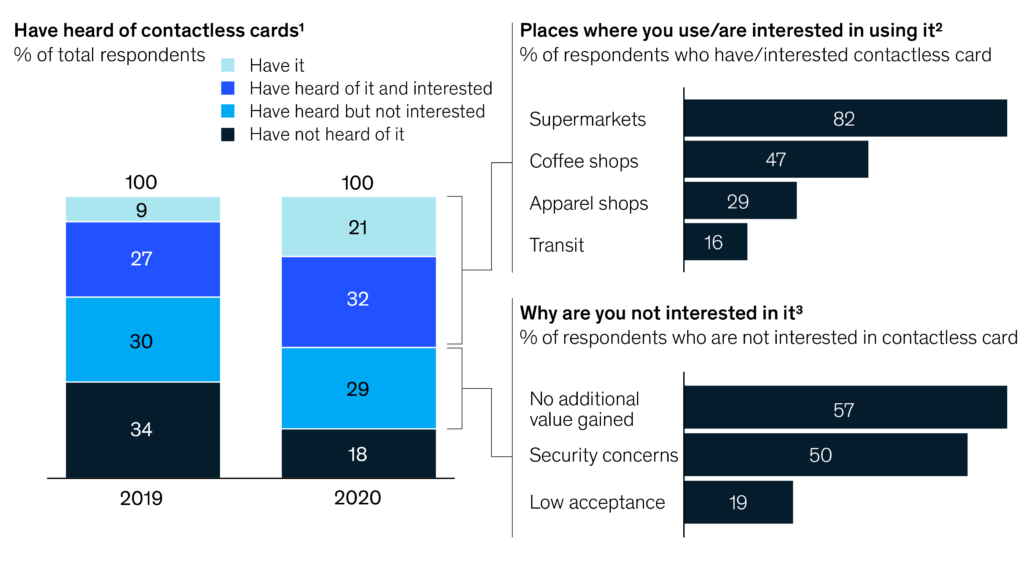
Data source: Mckinsey
These stats shed light on the “Digital First” approach to payment.
As payments evolve into a crucial differentiator and revenue driver, there can no longer be an afterthought of “if.” After all, in today’s fast-moving and unpredictable global environment, payment is the focal point of your business strategy, and digital innovation is a trusted way to prepare your treasury for the future.
And as a matter of fact, payment processing services are not merely a necessity. It’s much beyond that. It includes untold benefits for businesses.
Benefits of integrating payment processing
Payment processing services and businesses go hand in hand.
For retailers and software services, seamless payment services are unskippable for the success of their platform. So, here’s a breakdown of the many benefits of integrated payment processing.
1. Open wealth of new revenue streams
No doubt, monetizing your platform can open a wealth of new revenue streams. The possibilities are never-ending, from confining premium content behind a paywall to providing different payment systems based on customer usage.
One incredible prospect of a payment processing integration is an additional revenue stream through revenue sharing. Revenue sharing allows software businesses to earn money from the transaction fees their customers pay to accept credit cards through the integration. Actually, it’s the same types of costs that the software company pays to accept credit cards, but here, they are on the receiving end of the fees.
Moreover, integrated payment processing allows you to provide several types of payment models based on what’s ideal for your business. So, whatever the preference is, the core is the same: you have control over how payment works for your business. And you can easily choose and pursue new revenue streams through that control.
2. Increase the value of your brand
By establishing a convenient payment system in your business, you are automatically increasing the value of your platform.
The convenience, security, and reliability of a strong payment system is invaluable to the customers.
Not to forget, directly integrating payment processing into your platform eliminates the challenges customers face in entering and improving their experiences. Simply put, it increases the likelihood of customers buying from you.
So, by making payments easy and safe for your customers, you are expanding the value of your complete platform.
3. Reduce labor costs
Payment processing services are one of the ways you can save your business costs.
Payments will flow directly into the general ledger at the payment moment. This means that it’s no longer required to have a dedicated receivable employee on the payroll. Besides, paying an accountant to re-enter data from credit card transactions to reconcile accounts is unnecessary.
Therefore, you’ll save the cost and time spent on training employees to process payments as the process turns much simpler and easier.
4. Integrate seamlessly with your existing platform
A well-built payment processor will easily integrate with your platform.
But integrating doesn’t mean you have to change your model to adapt to the payment system – instead, the processor adjusts to you. Trusted and modern payment processing systems like GETTRX are adaptable and user-friendly so that you can integrate them into your platform seamlessly.
5. No more worries about security and compliance
By using secure payment processing options, you’ll save on those endless headaches of generating invoices while leveraging the benefits of integrated payments.
When you host payments, you’ll have to go through the tedious process of audits, and IT scans. It’s expensive, difficult to maintain, and resource-intensive. But, with a reliable payment processor, you don’t have to worry about it – your company never has to carry the onus of any personal and financial information.
You can sigh relief knowing your client’s data is secure without sweating the security details.
Similarly, choosing the right payment processor can be overwhelming, whether you’re new to the game or making a switch.
But, with untold payment processing platforms available today, choosing the right one might seem daunting. Fortunately, we are here to help you.
Here is how you can choose the best payment processing solution
Make sure your payment processor has a solid understanding of how your business works. Here are some helpful tips to get you pointed in the right direction. Let’s look!
1. PCI compliance
Security is imperative.
So, your payment provider must take all the necessary steps to integrate compliance with the PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). And, if they are not PCI compliant and cannot help your business complete the official PCI DSS Self Assessment Questionnaire to validate your compliance, then it’s a red flag; step back!
You must be wondering why it’s important.
Yes, it is because if a business is not compliant, they are putting itself and its customers at risk. Imagine a team that offers you a vast selection of payment solutions plus provides PCI DSS security professionals who can assist your business in achieving compliance.
2. Excellent customer support
Arguably the most unskippable factor that most merchants overlook as the payment processing is “behind the scenes.”
But what if something goes down unexpectedly? Will your payment provider be available when you need help?
3. Integrations
Does your business use accounting software, ERP or CRM? Or, maybe you have a front-end POS system that helps you in your business?
Therefore, by having a reliable integrated payment solution into your existing system, you will minimize human data entry errors and save time and money through automated reconciliation.
Helpful Tip – Not every integration will be a walk in the aisle, but your payment provider should be capable of assisting you to walk through your integrations or even offer to help you set up.
So, ensure your payment provider helps you make your integration quick and easy.
Our experts will work with you to ensure your systems are up to snuff.
4. No hidden fees
Before you put your finger on the payment processor, ensure your provider is transparent about fees.
Further, on top of standard Visa, Mastercard, and Amex, look for standard processing rates as cards have different costs. And providers need to include a fee schedule that makes these costs more transparent, whether that’s monthly fees, statement fees, batch and authorization fees.
Arrayed with this knowledge, you now have all the most relevant information to set up online payments for your business and select the best option for your company.
Hopefully, these considerations drive you straight to your next payment processing decision.
If you are still sitting on the fence about what payment processor to choose, want to switch payment service providers for a better integration or cost, or are a curious head – just get in touch. We are here for you.
Qn1. What is payment processing?
Payment processing is how businesses complete card (debit and credit) transactions. It includes expedited card transactions and payment gateways securely transmitting data so money from a customer’s issuing bank can be easily and quickly transferred to the merchant’s account. All this happens in seconds.
Qn2. What is a payment gateway?
A payment gateway is merchant services offered by an eCommerce application service provider that authorizes credit card or direct payment processing for online businesses, retailers, or traditional brick-and-mortar stores.
Qn3. What is a payment processor?
A payment processor is a system that allows financial transactions, commonly employed by a merchant, to manage transactions with customers from different channels like credit cards and debit cards or bank accounts. They are usually broken down into two types: front-end and back-end.
Qn4. How does a payment processor work?
The payment processor validates and approves the transaction. The customer’s bank sends money to the processor. The processor sends money to the merchant’s bank. Next, the processor sends the transaction’s status to the gateway – either approved or denied.
Qn5. What is a merchant account?
A merchant account is a bank account that enables businesses to accept payments in different ways, especially debit or credit cards. A merchant account is established under an agreement between an acceptor and a merchant acquiring bank to settle payment card transactions.
Qn6. What are merchant services?
Merchant services are a wide category of financial services for use by businesses. Its most specific use often refers to merchant processing services allowing a business to accept a transaction payment through a secure (encrypted) channel using the customer’s credit card, debit card, or NFC/RFID-enabled devices.
For more information on Payment Processing, check out these resources: Payment Processing Security, Challenges in Online Payment Processing, Credit Card Processing: A Guide for Merchants
Editor’s Note: This blog entry was originally published on September 9, 2022, and is updated on Feb 8, 2023.






